Vitamin D deficiency is also known as hypovitaminosis D. Vitamin D deficiency is very common and many people are unaware of it. Fortunately, vitamin D deficiency is easy to fix. Symptoms and signs of vitamin D deficiency could be helpful definitely, If you suspect that you may need more vitamin D based on this list, it’s best to talk to your doctor and get your blood levels checked.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that greatly affects our body, from ensuring calcium supply to our bones to strengthening our immune system. According to Dr. Michael Holick, a leading vitamin D researcher, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that 32% of adults and children in the United States, and approximately 1 billion people worldwide are suffering from vitamin D deficiency. Therefore, it is vital to look for signs of vitamin D deficiency.
Now, here are the most common signs of vitamin D deficiency, we want to tell you what we found.
1. Dark skin

If you have dark skin, you may need as much as 10 times more sun exposure to get the same amount of vitamin D as a person with pale skin. Your skin pigment acts as a natural sunscreen, so you need to spend more time in the sun as you have more pigment.
The melanin, which helps prevent skin cancers such as melanoma, can reduce the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D when exposed to the sun. People with darker skin have more melanin, allowing less sun exposure to enter the skin. This means that the body produces less vitamin D. In fact, it is well known that adults over the age of 65 with darker skin are at higher risk for vitamin D deficiency.
2. Anxiety and Depression

According to a study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, one of the hallmarks of vitamin D deficiency is depression. To confirm this theory, the researchers studied 80 elderly patients and found that people with low vitamin D levels were 11 times more vulnerable to depression.
Various psychological changes can occur as a result of vitamin D deficiency. Scientists say that the main symptoms associated with SAD (Seasonal Affective Disorder) are a result of changing levels of vitamin D. When there is less sunshine, SAD is a mood disorder that results in symptoms of depression during the winter months. This is caused by a sudden drop in the level of vitamin D in a person’s body.
Altering the level of vitamin D in the brain affects serotonin levels and affects a person’s mood. Low levels of serotonin are linked to depression. This is because serotonin is a chemical and neurotransmitter that helps regulate our sleep, appetite, moods, social behavior, and much more.
If you find yourself feeling more and more depressed, especially during the winter months, it may be because you have a vitamin D deficiency.
If this is the case, consider talking to your doctor about vitamin D supplements that can help boost your body’s vitamin D levels and improve your mood.
3. Signs of vitamin D deficiency Hair loss
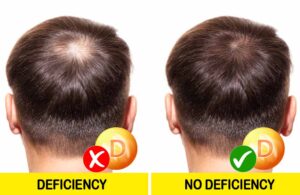
Hair loss is often caused by stress and is definitely a common cause. Many other factors can cause hair loss and vitamin D deficiency is one of them. Lack of this vitamin can lead to impaired hair cycling process, thinning hair, and hair loss. Vitamin D is an essential component of the hair growth process in hair loss and can be used as a supplement to treat hair loss.
4. Slow wound healing
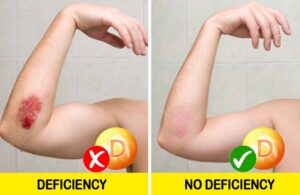
Healing wounds after surgery, injury or infection can be a sign that your vitamin D level is too low. A study has found that 12-week vitamin D supplementation significantly reduces the risk of injury among patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Scientists believe that vitamin D has a positive effect on stabilizing blood glucose and cholesterol levels, according to researchers. If your wounds are healing slowly (especially if you have diabetes), pay attention to these vitamin levels in your body.
5. You are at least 50

Vitamin D is a very common risk factor in adults. Adults are at a higher risk of developing vitamin D deficiency because of their reduced ability to synthesize vitamin D in direct sunlight as they enter adulthood. In addition, vitamin D is active in the body’s kidneys, a function that decreases with age. Adults are less likely to exercise and live an active lifestyle as they get older. They tend to stay inside longer.
According to the International Association for Clinical Densitometry, about 95% of senior citizens suffer from vitamin D deficiency. The reason is not only that they spend a lot of time indoors, but another reason is also that they produce less vitamin D even exposed to the sun. They say an adult over the age of 70 produces 30% less vitamin D than a young person exposed to the same sun.
Scientists say you need about 30 minutes of sun exposure at least twice a week to get the amount of vitamin D you need. According to the Food and Nutrition Board, the average vitamin D intake for a person over the age of 50 is 200 international units (IU) for men and women.
Men and women between the ages of 50 and 70 should take 400 international units daily, and after the age of 70, both men and women should increase this consumption to 600 IU. There are many supplements on the market that can be taken by adults to increase vitamin D levels.
6. Weakened immune system

Vitamin D plays a major role in supporting our immune system. It interacts directly with the cells responsible for fighting infection. Unknowingly, long before doctors discovered antibiotics, they began treating these infections with vitamins.
For example, tuberculosis patients were sent to sanatoriums exposed to sunlight, which, at the time, doctors thought killed the infection directly. Therefore, if you regularly suffer from viral infections such as the common cold or flu, low vitamin D levels may be the cause. Several large-scale observational studies have shown an association between deficiency and respiratory tract infections such as the common cold, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
7. Bone pain
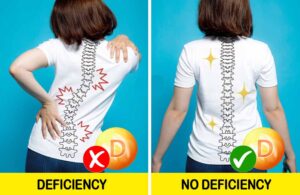
Researchers have found that people with deficiency are more likely to have back pain. Including severe back pain that limits their daily activities. Vitamin D helps maintain bone health in a variety of ways. Lack of vitamin D impairs the body’s ability to deliver calcium to bone tissue, which can lead to osteomalacia or weakening of the bones.
Vitamin D deficiency can be associated with a variety of musculoskeletal aches, especially tibial bone pain and tenderness. It is recommended to ensure that you consume the required amount of vitamin D daily to prevent related diseases such as bone pain, fractures, and osteoporosis.
8. Muscle pain
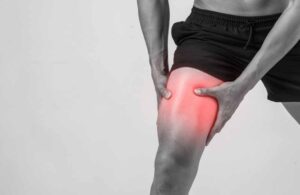
Vitamin D affects not only our bones but also our muscles. Lack of this vitamin causes severe muscle pain, reduced muscle mass, and poor muscle recovery after strenuous physical activity. Decreased vitamin D levels can cause chronic widespread pain in the body, which is a major symptom of fibromyalgia. Several studies have found that taking high doses of vitamin D supplements can reduce a variety of pains in people with deficiencies.
9. Fatigue and weakness

This is not normal fatigue, because we often tend to attribute fatigue and tiredness to a busy lifestyle or lack of sleep. If you regularly get at least eight hours of sleep and are still tired, a lack of vitamin D in the body seems to be linked to this. A study that observed the effect of vitamin D supplementation on patients with fatigue revealed that the symptoms of fatigue were significantly reduced after the normalization of vitamin D levels.
10. Being overweight, obese, or overweight

Researchers explain that vitamin D is fat-soluble, which means that the body accumulates it. Therefore, if you are overweight or obese, your body needs more vitamin D than the average person. The same is true for those with a lot of muscle and body mass.
11. Sweaty head

Various symptoms can indicate that your vitamin D level is low. According to researchers, sweating head is one of the first signs of vitamin D deficiency. They say many doctors used to ask new mothers if their newborn was experiencing sweating head. Excessive sweating in newborns is still described as an early symptom of vitamin D deficiency due to neuromuscular irritation.
12. Gut problems
As mentioned earlier, vitamin D is fat-soluble, so if you have gastrointestinal problems that affect your body’s ability to store fat, you may be less likely to absorb fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin D, Certain gut conditions that are common include Crohn’s, celiac and non-celiac gluten sensitivity, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Sources of Vitamin D
According to Canadian dietitians, the following are sources of vitamin D:
Grain products, plain yogurt, orange juice, deli meat, beef liver, pork, salmon, eggs, vegetables and fruits, mackerel, tuna, cheese, egg yolk, and cod liver oil.
Remember, if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, see your doctor because you have a vitamin D deficiency.
Some people are at higher risk of developing vitamin D deficiency. These people include the elderly, people with milk allergies, people with dark skin, or those who follow a vegan diet.
Symptoms associated with vitamin D deficiency include cardiovascular disease, cancer, asthma in children, cognitive impairment in adults, and more.
Did you know that more than 90% of skin cancers are caused by sun exposure? This is why scientists often debate the best way to get vitamin D. Although vitamin D comes from the sun, prolonged exposure to the sun can cause other serious health problems and risks that can lead to cancer.
Excessive exposure to the sun causes harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays to reach the inner layers of a person’s body. This causes sunburn and can destroy or even damage skin cells. As we mentioned above, a small amount of ultraviolet light is good for us (because it produces vitamin D), excessive sun exposure can lead to early aging, skin cancer, weakened immune system, and much more.
This is why doctors recommend eating a diet rich in vitamin D. Vitamin D supplements are becoming more and more popular as many foods lack vitamin D. Talk to your doctor today about the best ways to boost your vitamin D levels. Your doctor may recommend a vitamin D supplement.
You can increase sun exposure or by eating vitamin-D-rich foods such as fatty fish or strong dairy products. Or if you eliminate all the animal products, you can find various vitamin D supplements on Amazon.
Now, you know the signs of vitamin D deficiency and make it easy to see your doctor if you are concerned.
What methods are you trying to get more vitamin D from?
Did you enjoy our list of signs of vitamin D deficiency? For more articles like this, click the similar button below.
Tell us about your experience in the comments section below.
Don’t forget to like and share this article with your friends to stay healthy, click subscribe to join us for a healthier lifestyle.
Thanks for reading!
Preview photo credit Adobe Stock
Read more: 11 Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Share This Article





